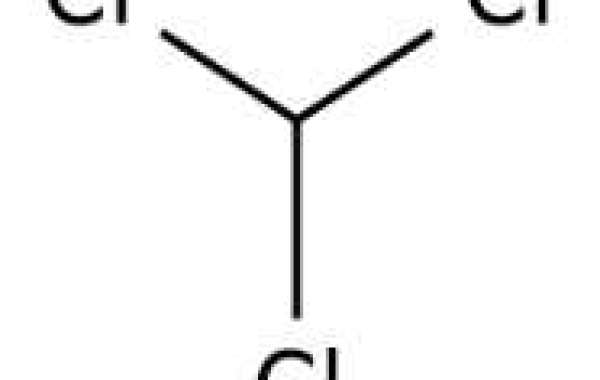
Chloroform is well absorbed, metabolized, and eliminated by oral, inhalation, or cutaneous exposure in mammals and is widely distributed throughout the organism by circulation, preferentially in adipose tissue and the brain due to its lipid solubility. After inhalation exposure, the human half-life is 7.9 hours. An oral exposure study found that most chloroform doses disappeared within 8 hours of exposure.
Chloroform is mainly metabolized in the liver. The main metabolite is carbon dioxide. In vivo oxidation pathway also produces active metabolites including phosgene, while reduction pathway produces dichloromethyl carbene radical. Both pathways proceed through cytochrome P450-dependent enzymatic activation steps, and their balance depends on species, tissue, dose, and oxygen tension. Phosgene is produced by chloroform oxidation, dechlorination to trichloroethanol, and spontaneous dehydrogenation of trichloroethanol.
Chloroform toxicity is caused by its metabolites. Transplacental transfer of chloroform has been reported in mouse and rat fetal blood, and it is expected to be present in human colostrum and excreted by mature breast milk.
In animals and humans, inhalation, skin and oral absorption are considered to be 80%, 10% and 100%, respectively.
It presents as a large mediastinal lesion characterized by diffuse proliferation of medium to large cells, often with well-defined cytoplasm, sometimes resembling lacunar cells. Many cases showed a network of collagen fibers rather than concentric fibers immunohistochemically, PMLBCL expressed pan-B cell markers and CD45, usually positive for CD23, weakly positive for CD30, and often positive for BCL6 and MUM1, but lacking CD10 and surface immunoglobulin.
These complex or sequential tumors must be diagnosed as such, indicating a histological component; They should not be classified as B-cell lymphoma.
In contrast to CHL and primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma, most of these cases occurred in the mediastinum and were mostly male.