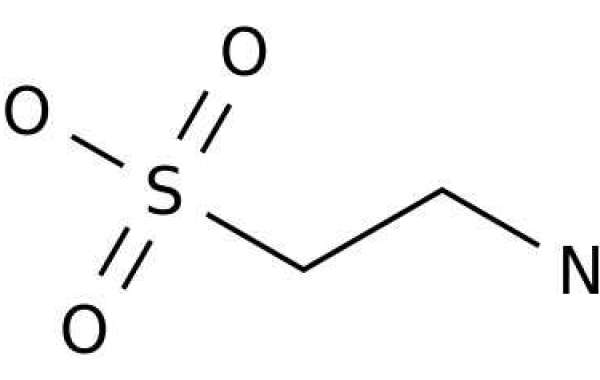
Taurine is an organic compound known as an amino acid. Amino acids are the protein building blocks of the human body. Some experts believe whats taurine has health benefits, but researchers need to carry out more studies to confirm these claims. Today, manufacturers add taurine to infant formula, nutritional supplements, and energy drinks. Taurine also occurs naturally in a range of animal foods, including seafood, beef, and chicken. However, vegetarian and vegan foods tend to be deficient in taurine.
Some researchers and healthcare professionals believe that taurine may be useful in managing conditions such as epilepsy and diabetes. Although scientists need to carry out more research, in this article, we analyze the health benefits and potential risks of taurine consumption.
What is taurine?
Taurine is an amino acid, which is a building block of human proteins. Researchers have found Trusted Source taurine in the brain, spinal cord, heart and muscle cells, skeletal muscle tissue, and retinas. Taurine is also present in leukocytes or white blood cells, that reside in the immune system.The human body can produce whats taurine, but obtaining it from dietary sources or supplements is necessary to maintain optimum levels. It is important to note that vegetarian and vegan foods do not contain much taurine. As a result, it may be especially important for people who follow these diets to take supplements.
Why do we need taurine?
Taurine plays an essential role in protecting cells from damage. Some studiesTrusted Source have suggested that taurine can act as a neurotransmitter. These are chemical messengers present in the central nervous system.
Some research suggests that taurine plays a role in brain development and the prevention of birth abnormalities. For example, when taurine levels drop, mice experience defects in mitochondria and heart and muscle developmentTrusted Source. Mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell, producing the energy it needs to function. In other rat and mouse studies, researchers have shown that when taurine loses its effect in the retina, the rodents show severe cell degeneration in that area.
Potential health benefits
In the sections below, we take a look at what the existing research suggests about whats taurine and its possible role in several conditions. Scientists need to carry out further research in humans, however, before doctors can begin recommending taurine as a treatment option.