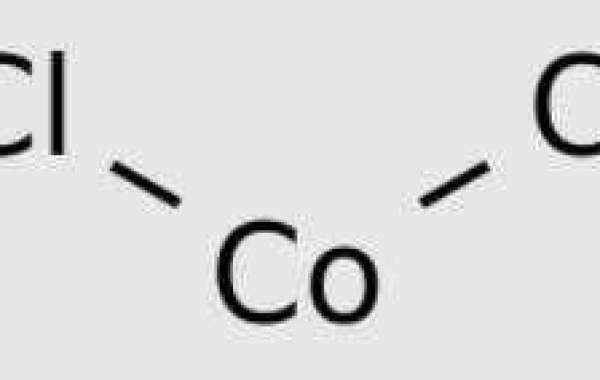
CoCl2 is one of the most common forms of chloride found in the laboratory today. Its chemical formula is CoCl2, and its molecular weight is 129.833 g/mol. This compound is most commonly supplied in the form of CoCl2 hexahydrate or anhydrous CoCl2.
CoCl2 hexahydrate (II)
CoCl2 hexahydrate (II) appears bright pink. The chemical formula of this compound is CoCl2 · 6H2O. If swallowed or applied directly on the skin, it is harmful and usually stable at room temperature. Hexahydrate is one of the most common forms of cobalt used in laboratory environments to date. Noah Chemicals supplies ACS reagent grade CoCl2 hexahydrate.
Anhydrous CoCl2
Anhydrous CoCl2, also known as CoCl2, is a beautiful sky blue. It is usually supplied in the form of lead and should be handled with care because it is a suspected carcinogen. Noah Chemical Company supplies anhydrous CoCl2 with a purity of 99%.
Application of CoCl2
CoCl2 will change color with the change of humidity, so there is a color difference between its anhydrous and hexahydrate forms. It is often used as an indicator for water desiccants. CoCl2 is a weak Lewis acid.
It is also a powerful intermediate compound. CoCl2 is a common precursor of other cobalt compounds, which is prone to oxidation and is typically used in the presence of a catalyst. It is an essential precursor for cobalt diene and tetraalkyl. CoCl2 is said to be dynamically inert.
Commercially, CoCl2 is commonly used in the manufacturing of sealants, adhesives, and adhesives. It is also used for electroplating, especially for objects coated with cobalt metal. Metal surface treatment is another common industrial use of this compound.
Cobalt is essential for most advanced forms of life, but exceeding a few milligrams per day is harmful. Although cobalt compounds rarely cause poisoning, long-term ingestion of these compounds, even at doses far below lethal doses, can cause serious health problems. In 1966, in Canada, the addition of cobalt compounds to stabilize the beer foam led to a special form of toxin induced cardiomyopathy, which was later called beer drinker cardiomyopathy.
In addition, according to the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) monograph, CoCl2 is suspected to be carcinogenic (i.e. potentially carcinogenic, IARC Group 2B).
From 2005 to 2006, CoCl2 was the eighth most common allergen in patch tests (8.4%).