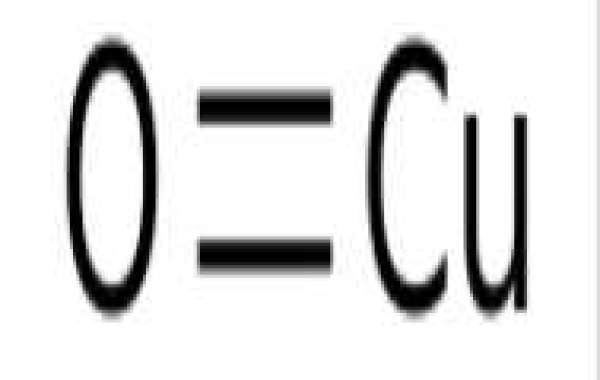Cupric oxide, or copper (II) oxide, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuO. Cupric oxide is used as a precursor in many copper-containing products such as wood preservatives and ceramics.
Copper(II) oxide formula or cupric oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula CuO. A black solid, it is one of the two stable oxides of copper, the other being Cu2O or copper(I) oxide (cuprous oxide). As a mineral, it is known as tenorite. It is a product of copper mining and the precursor to many other copper-containing products and chemical compounds.
It is produced on a large scale by pyrometallurgy, as one stage in extracting copper from its ores. The ores are treated with an aqueous mixture of ammonium carbonate, ammonia, and oxygen to give copper(I) and copper(II) ammine complexes, which are extracted from the solids. These complexes are decomposed with steam to give CuO.
It can be formed by heating copper in air at around 300–800°C:
2 Cu + O2 → 2 CuO
For laboratory uses, pure copper(II) oxide formula is better prepared by heating copper(II) nitrate, copper(II) hydroxide, or basic copper(II) carbonate.
Copper(II) oxide formula dissolves in mineral acids such as hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid or nitric acid to give the corresponding copper(II) salts:[4]
CuO + 2 HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + H2O
CuO + 2 HCl → CuCl2 + H2O
CuO + H2SO4 → CuSO4 + H2O
In presense of water It reacts with concentrated alkali to form the corresponding cuprate salts:
2 MOH + CuO + H2O → M2[Cu(OH)4]
2 NaOH + CuO + H2O → Na2[Cu(OH)4]
Copper(II) oxide formula belongs to the monoclinic crystal system. The copper atom is coordinated by 4 oxygen atoms in an approximately square planar configuration.
As a significant product of copper mining, copper(II) oxide formula is the starting point for the production of other copper salts. For example, many wood preservatives are produced from copper oxide.[3]
Cupric oxide is used as a pigment in ceramics to produce blue, red, and green, and sometimes gray, pink, or black glazes.
Copper(II) oxide formula is an oxide of copper. It occurs naturally as the mineral tenorite. Copper(II) oxide formula is used as a pigment in ceramics, in the production of rayon, as a dietary supplement, in dry and wet cell batteries, for welding copper alloys, and as a semiconductor. Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. Copper is an essential elements in plants and animals as it is required for the normal functioning of more than 30 enzymes. It occurs naturally throughout the environment in rocks, soil, water, and air.
Copper II Oxide (CuO) is better known as Cupric Oxide or black copper oxide. It is found in nature in the mineral tenorite and cuprite. The other stable form of copper oxide is Copper I Oxide, cuprous oxide, but this oxide is readily oxidized to cupric oxide in moist air. The primary use of CuO is to make copper salts and compounds but finds use in other applications such as pottery glazes to produce blue, green or red colors. Its use in fireworks and pyrotechnics produces a moderate blue color when used with chlorates and other chlorinated oxidizers such as perchlorates.