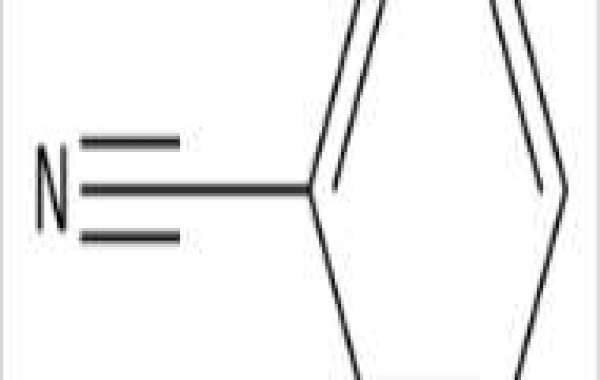
Benzonitrile appears as a clear colorless liquid with an almond-like odor. Flash point 161 °F. Denser than water and slightly soluble in water. Used as a specialty solvent and to make other chemicals.
Benzonitrile is a nitrile that is hydrogen cyanide in which the hydrogen has been replaced by a phenyl group. It is a member of benzenes and a nitrile.
Benzonitrile is a natural product found in Arctostaphylos uva-ursi with data available.
Benzonitrile is a stable compound to pyrolysis, and its decomposition starts above 550°C with a very low decomposition rate. A study performed in a flow reactor on N2 saturated with benzonitrile [8] in the temperature range 550–600°C showed that the main pyrolysis products of this compound are HCN, benzene, monocyanodiphenyls, dicyanodiphenyls, and dicyanobenzenes as well as char. The reaction takes place by a radicalic mechanism, starting with the following initiation reaction:
H5C6−CN→H4C6•−CN+H•
Benzonitriles and Phenoxy Acids
Benzonitriles and phenoxy acids are widely applied as salts or esters, but they are hydrolyzed to their respective phenols or acids in the matrix. Extraction of residues from soil and water is commonly performed at acidic pH with organic solvents of medium polarity. Initially, the extraction of these herbicides from vegetable matter was done with aqueous solutions at basic pH, followed by extraction with organic solvents.At present, different techniques such as SPME for aqueous samples, UAE for soil and MAE or PLE for plant samples are often used. QuEChERS is also used for the extraction of acidic herbicides from soil and plant samples after alkaline hydrolysis with sodium hydroxide.
A clean-up step after extraction is required in most cases to allow the determination of herbicides at trace levels. Among the clean-up techniques used, the liquid–liquid partition at basic pH has been employed, but the most common procedure is solid-phase extraction (SPE) with cartridges or columns using sorbents of different characteristics depending on the selected herbicides. Sorbents such as Florisil, silica, alumina and C18 are used for the determination of benzonitrile and phenoxyacid herbicides. The use of graphitized carbon black (GCB) is adequate for the removal of non-polar and oxygen-containing compounds due to hydrophobic, electronic and ion-exchange interactions. The combination of GCB and aminopropyl adsorbent is effective to remove pigments and organic acids from wheat and soil samples.
Benzonitriles can be determined directly by GC, but the sensitivity and reproducibility achieved are poor. Various derivatives overcome these problems and diazomethane and heptafluorobutyric anhydride were the reagents most often employed.
In the last years, new methods for analysis of acidic herbicides in environmental samples are used. Injection port derivatization following ion-pair hollow fiber liquid- phase microextraction has been developed for the determination of acid herbicides in water samples.